👩💻중앙대 자료구조 assignment#3_Find MST using Kruskal alg.(C언어, C++)
2022. 6. 1. 23:59ㆍ자료구조
728x90
👻kruskal 알고리즘은 대회에서 자주 출제된다!
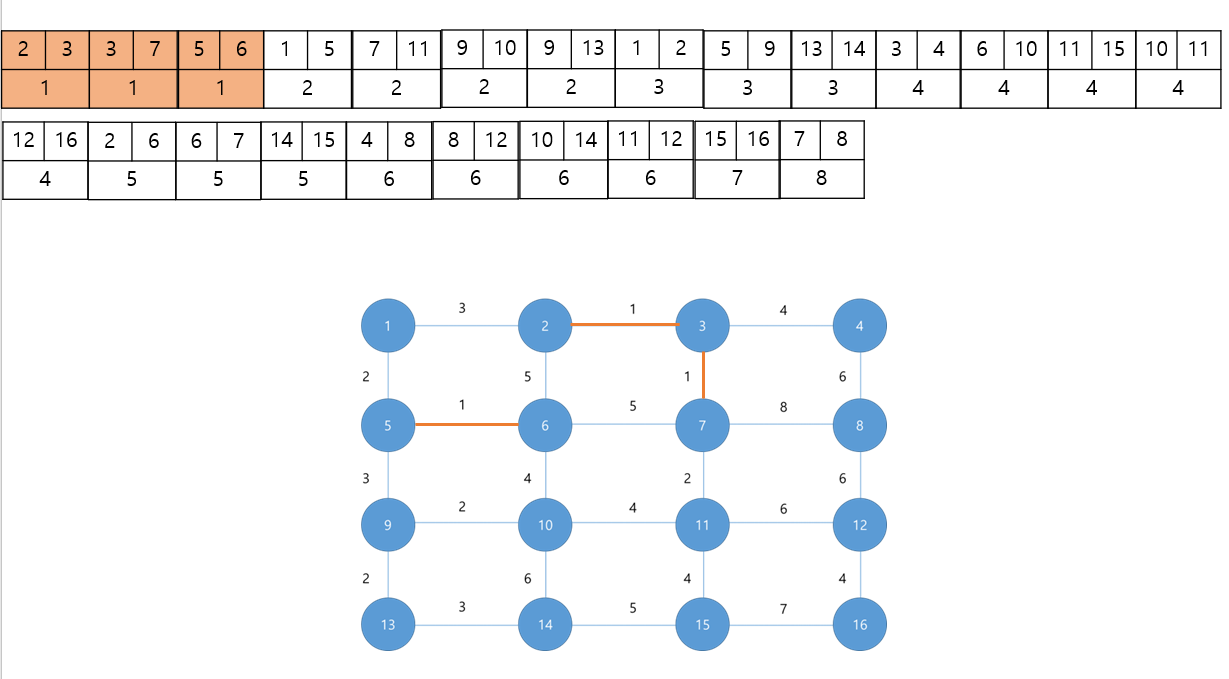
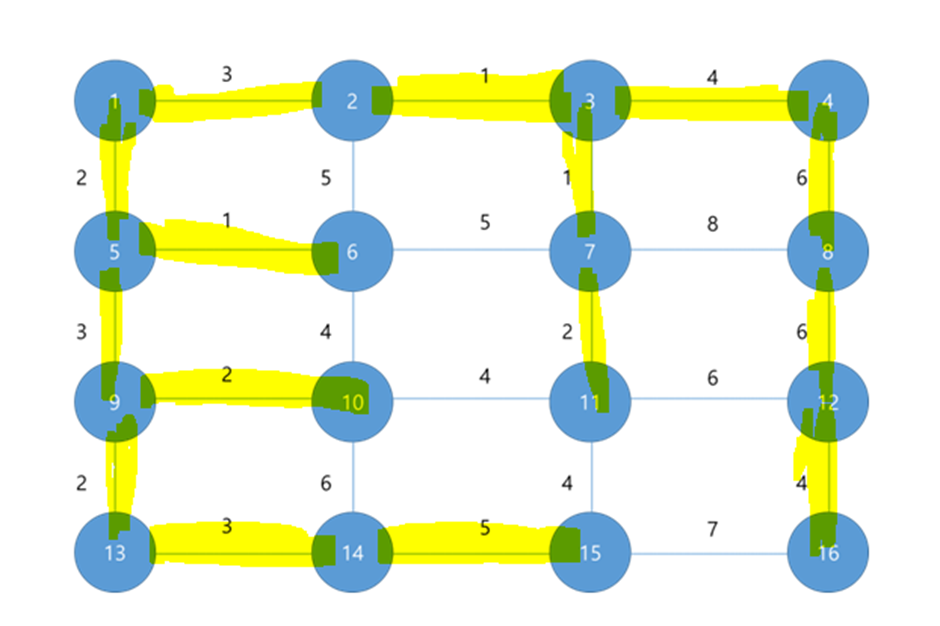
- Implements the following graph as an adjacency list.
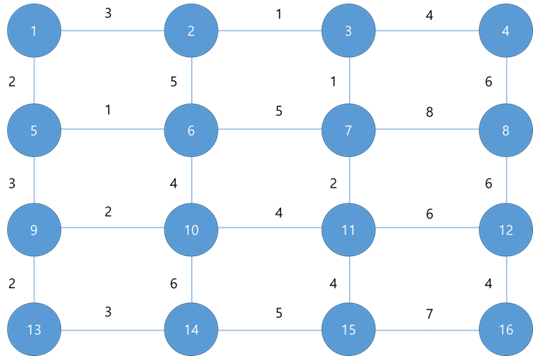
2. Find the minimum spanning tree (MST) using the Kruskal method.
3. Find the shortest path from vertex # 1 in the graph to all vertices.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
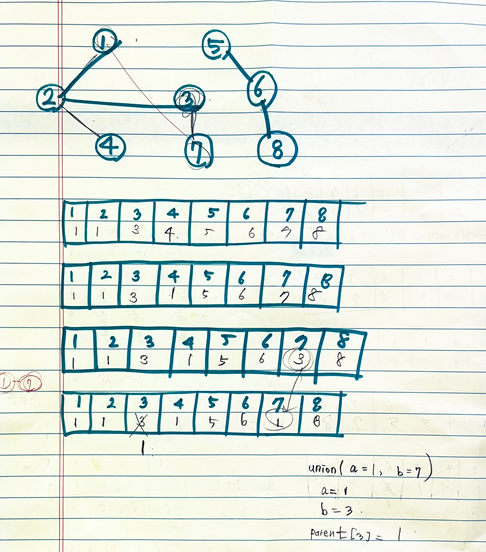
👻노드가 같은 그래프에 속해있는지 확인하기 위해 union- find(합집합 찾기) 알고리즘을 먼저 알아야 한다.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AMByrd53PHM
https://m.blog.naver.com/ndb796/221230967614
17. Union-Find(합집합 찾기)
Union-Find(유니온-파인드)는 대표적인 그래프 알고리즘입니다. 바로 '합집합 찾기'라는 의미를 가진 알...
blog.naver.com
#include <stdio.h>
//Union_Find
int getParent(int parent[], int x) {
if (parent[x] == x)
return x;
return parent[x] = getParent(parent, parent[x]);
}
//각 부모 노드를 합칩니다.
void unionParent(int parent[], int a, int b) {
a = getParent(parent, a);
b = getParent(parent, b);
if (a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else {
parent[a] = b;
}
}
//같은 부모 노드를 가지는지 확인합니다.
//같은 그래프에 속해있는지 확인하는 것과 동일
int findParent(int parent[], int a, int b) {
a = getParent(parent, a);
b = getParent(parent, b);
if (a == b)return 1;
else return 0;
}
int main(void) {
int parent[9];
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
unionParent(parent, 1, 2);
unionParent(parent, 2, 3);
unionParent(parent, 5, 6);
unionParent(parent, 6, 8);
unionParent(parent, 1, 8);
printf("1과 3는 연결되어있나요? %d\n", findParent(parent, 1, 3));
printf("3과 8은 연결되어있나요? %d\n", findParent(parent, 3, 8));
}
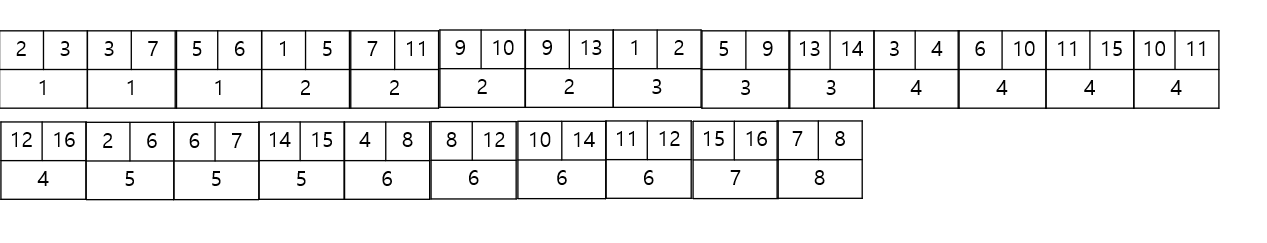
👻비용을 기준으로 오름차순으로 정렬

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//부모 노드를 가져옴
int getParent(int parent[], int x) {
if (parent[x] == x)
return x;
return parent[x] = getParent(parent, parent[x]);
}
//각 부모 노드를 합칩니다.
void unionParent(int parent[], int a, int b) {
a = getParent(parent, a);
b = getParent(parent, b);
if (a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else {
parent[a] = b;
}
}
//같은 부모 노드를 가지는지 확인합니다.
//같은 그래프에 속해있는지 확인하는 것과 동일
int findParent(int parent[], int a, int b) {
a = getParent(parent, a);
b = getParent(parent, b);
if (a == b)return 1;
else return 0;
}
//간선 클래스 선언
class Edge {
public:
int node[2]; //서로 연결된 두개의 노드정보
int distance;
Edge(int a, int b, int distance) {
this->node[0] = a;
this->node[1] = b;
this->distance = distance;
}
bool operator <(Edge &edge) {
return this->distance < edge.distance;
//거리가 작은 순으로 출력
}
};
int main(void) {
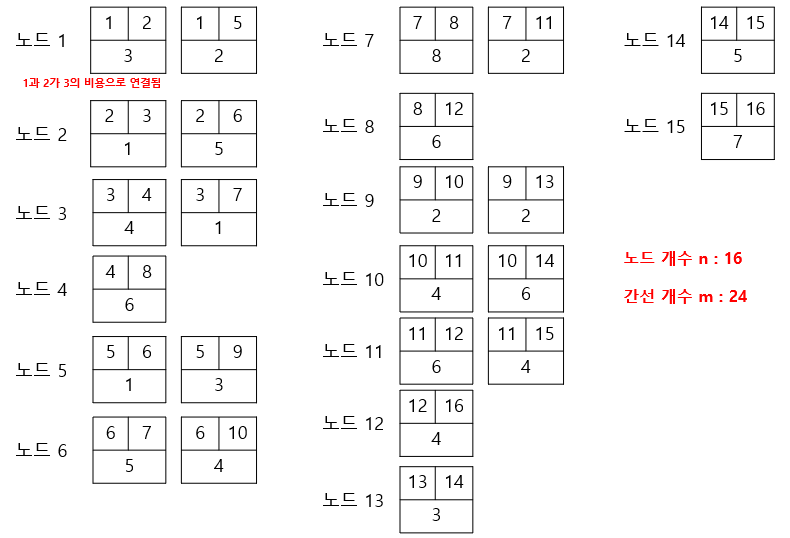
const int n = 16;//노드개수
const int m = 24; //간선개수
//24 79 - 55 = 24
vector<Edge> v;
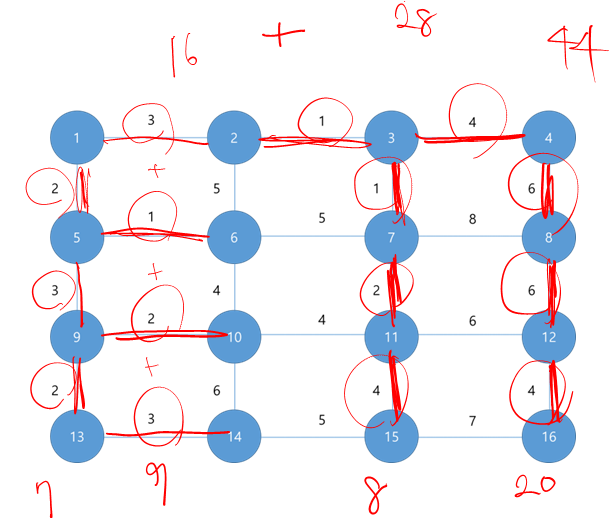
v.push_back(Edge(1, 2, 3)); //1과 2가 비용이 3인 간선으로 연결됨
v.push_back(Edge(1, 5, 2));
v.push_back(Edge(2, 6, 5));
v.push_back(Edge(2, 3, 1));
v.push_back(Edge(3, 7, 1));
v.push_back(Edge(3, 4, 4));
v.push_back(Edge(4, 8, 6));
v.push_back(Edge(5, 6, 1));
v.push_back(Edge(5, 9, 3));
v.push_back(Edge(6, 7, 5));
v.push_back(Edge(6, 10, 4));
v.push_back(Edge(7, 8, 8));
v.push_back(Edge(7, 11, 2));
v.push_back(Edge(8, 12, 6));
v.push_back(Edge(9, 10, 2));
v.push_back(Edge(9, 13, 2));
v.push_back(Edge(10, 11, 4));
v.push_back(Edge(10, 14, 6));
v.push_back(Edge(11, 12, 6));
v.push_back(Edge(11, 15, 4));
v.push_back(Edge(12, 16, 4));
v.push_back(Edge(13, 14, 3));
v.push_back(Edge(14, 15, 5));
v.push_back(Edge(15, 16, 7));
//간선의 비용을 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
sort(v.begin(), v.end()); //<algorithm>에 포함
//각 정점이 포함된 그래프가 어디인지 저장
int parent[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
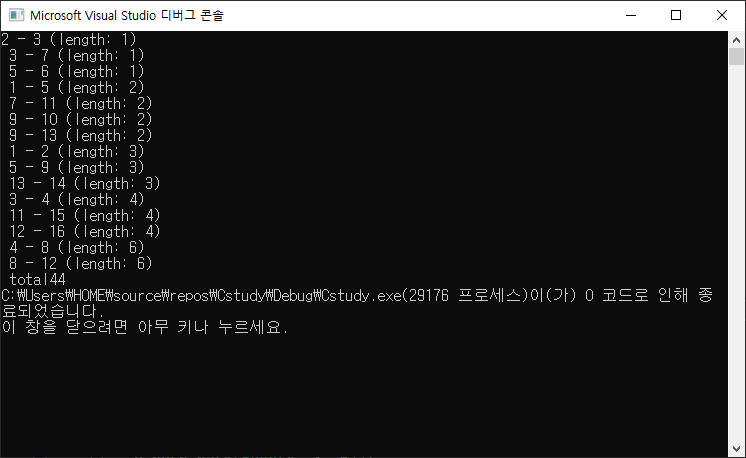
printf("Find the shortest path from vertex #1 in the graph to all vertices.\n");
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
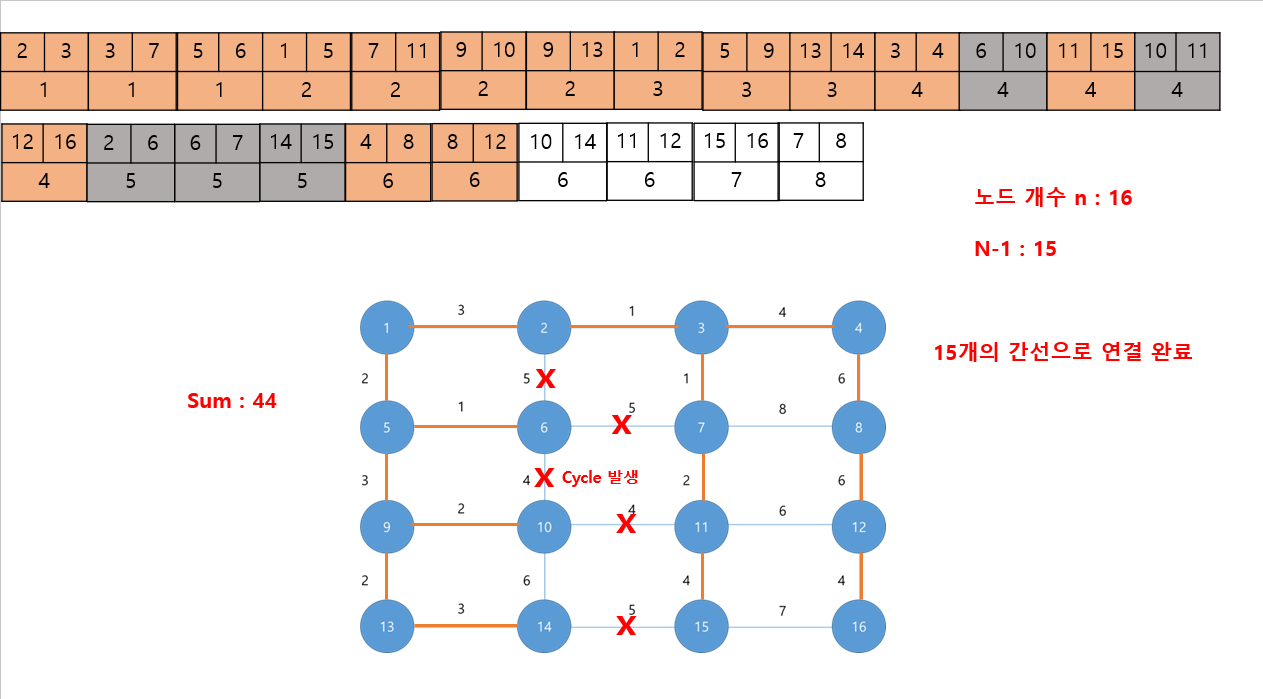
//사이클이 발생하지 않는 경우 그래프에 포함
if (!findParent(parent, v[i].node[0] - 1, v[i].node[1] - 1)) {
sum += v[i].distance; //거리총합에 저장
printf("%d - %d (length: %d)\n ", v[i].node[0], v[i].node[1], v[i].distance);
unionParent(parent, v[i].node[0] - 1, v[i].node[1] - 1);//두개의 노드 연결
}
}
printf("total%d", sum);
//return 0;
}
👻망했다. C++라이브러리 사용하지 말라고 하셔서 C로 다시 구현해야된다. 왕귀찮다.

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int total_cost;
struct Edge
{
int Source;
int Destination;
int Weight;
};
struct Graph
{
int VerticesCount;
int EdgesCount;
struct Edge* Edge;
};
struct Subset
{
int Parent;
int Rank;
};
struct Graph* CreateGraph(int verticesCount, int edgesCoun)
{
struct Graph* graph = (struct Graph*)malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->VerticesCount = verticesCount;
graph->EdgesCount = edgesCoun;
graph->Edge = (struct Edge*)malloc(graph->EdgesCount * sizeof(struct Edge));
return graph;
}
int Find(struct Subset subsets[], int i)
{
if (subsets[i].Parent != i)
subsets[i].Parent = Find(subsets, subsets[i].Parent);
return subsets[i].Parent;
}
void Union(struct Subset subsets[], int x, int y)
{
int xroot = Find(subsets, x);
int yroot = Find(subsets, y);
if (subsets[xroot].Rank < subsets[yroot].Rank)
subsets[xroot].Parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].Rank > subsets[yroot].Rank)
subsets[yroot].Parent = xroot;
else
{
subsets[yroot].Parent = xroot;
++subsets[xroot].Rank;
}
}
int CompareEdges(const void* a, const void* b)
{
struct Edge* a1 = (struct Edge*)a;
struct Edge* b1 = (struct Edge*)b;
return a1->Weight > b1->Weight;
}
void Print(struct Edge* result, int e)
{
for (int i = 0; i < e; ++i) {
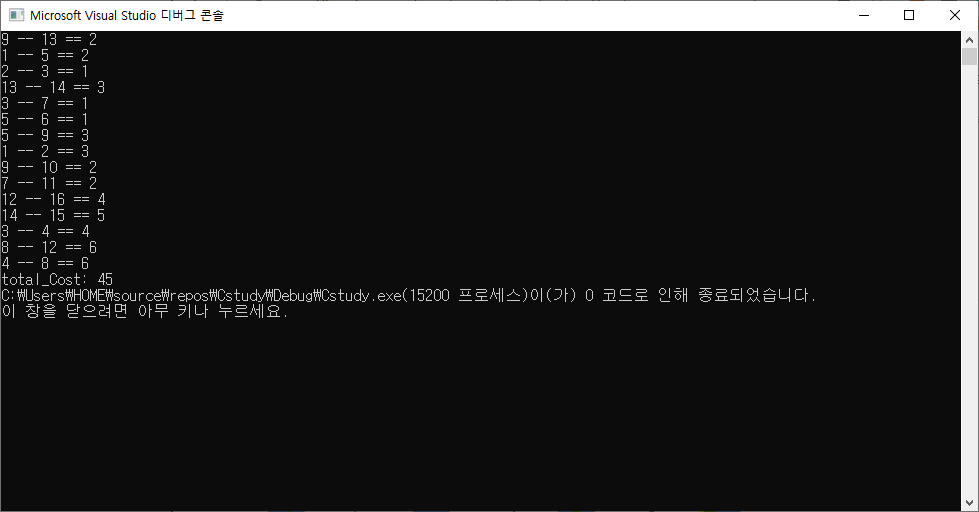
printf("%d -- %d == %d\n", result[i].Source, result[i].Destination, result[i].Weight);
total_cost += result[i].Weight;
}
}
void Kruskal(struct Graph* graph)
{
int verticesCount = graph->VerticesCount;
struct Edge* result = (struct Edge*)malloc(sizeof(result) * verticesCount);
int i = 0;
int e = 0;
qsort(graph->Edge, graph->EdgesCount, sizeof(graph->Edge[0]), CompareEdges);
struct Subset* subsets = (struct Subset*) malloc(verticesCount * sizeof(struct Subset));
for (int v = 0; v < verticesCount; ++v)
{
subsets[v].Parent = v;
subsets[v].Rank = 0;
}
while (e < verticesCount - 1)
{
struct Edge nextEdge = graph->Edge[i++];
int x = Find(subsets, nextEdge.Source);
int y = Find(subsets, nextEdge.Destination);
if (x != y)
{
result[e++] = nextEdge;
Union(subsets, x, y);
}
}
Print(result, e);
}
void main() {
int verticesCount = 16;
int edgesCount = 24;
struct Graph* graph = CreateGraph(verticesCount, edgesCount);
// Edge 0-1
graph->Edge[0].Source = 0;
graph->Edge[0].Destination = 1;
graph->Edge[0].Weight = 3;
// Edge 0-4
graph->Edge[1].Source = 0;
graph->Edge[1].Destination = 4;
graph->Edge[1].Weight = 2;
// Edge 1-2
graph->Edge[2].Source = 1;
graph->Edge[2].Destination = 2;
graph->Edge[2].Weight = 1;
// Edge 2-3
graph->Edge[3].Source = 2;
graph->Edge[3].Destination = 3;
graph->Edge[3].Weight = 4;
// Edge 2-6
graph->Edge[4].Source = 2;
graph->Edge[4].Destination = 6;
graph->Edge[4].Weight = 1;
// Edge 4-5
graph->Edge[5].Source = 4;
graph->Edge[5].Destination = 5;
graph->Edge[5].Weight = 1;
// Edge 4-8
graph->Edge[6].Source = 4;
graph->Edge[6].Destination = 8;
graph->Edge[6].Weight = 3;
// Edge 5-6
graph->Edge[7].Source = 5;
graph->Edge[7].Destination = 6;
graph->Edge[7].Weight = 5;
// Edge 6-7
graph->Edge[8].Source = 6;
graph->Edge[8].Destination = 7;
graph->Edge[8].Weight = 8;
// Edge 6-10
graph->Edge[9].Source = 6;
graph->Edge[9].Destination = 10;
graph->Edge[9].Weight = 2;
// Edge 7-11
graph->Edge[10].Source = 7;
graph->Edge[10].Destination = 11;
graph->Edge[10].Weight = 6;
// Edge 8-9
graph->Edge[11].Source = 8;
graph->Edge[11].Destination = 9;
graph->Edge[11].Weight = 2;
// Edge 8-12
graph->Edge[12].Source = 8;
graph->Edge[12].Destination = 12;
graph->Edge[12].Weight = 2;
// Edge 9-10
graph->Edge[13].Source = 9;
graph->Edge[13].Destination = 10;
graph->Edge[13].Weight = 4;
// Edge 9-13
graph->Edge[14].Source = 9;
graph->Edge[14].Destination = 13;
graph->Edge[14].Weight = 6;
// Edge 10-11
graph->Edge[15].Source = 10;
graph->Edge[15].Destination = 11;
graph->Edge[15].Weight = 6;
// Edge 10-14
graph->Edge[16].Source = 10;
graph->Edge[16].Destination = 14;
graph->Edge[16].Weight = 4;
// Edge 11-15
graph->Edge[17].Source = 11;
graph->Edge[17].Destination = 15;
graph->Edge[17].Weight = 4;
// Edge 12-13
graph->Edge[18].Source = 12;
graph->Edge[18].Destination = 13;
graph->Edge[18].Weight = 3;
// Edge 13-14
graph->Edge[19].Source = 13;
graph->Edge[19].Destination = 14;
graph->Edge[19].Weight = 5;
// Edge 14-15
graph->Edge[20].Source = 14;
graph->Edge[20].Destination = 15;
graph->Edge[20].Weight = 7;
// Edge 3-7
graph->Edge[21].Source = 3;
graph->Edge[21].Destination = 7;
graph->Edge[21].Weight = 6;
// Edge 5-9
graph->Edge[22].Source = 5;
graph->Edge[22].Destination = 9;
graph->Edge[22].Weight = 4;
// Edge 1-5
graph->Edge[23].Source = 1;
graph->Edge[23].Destination = 5;
graph->Edge[23].Weight = 5;
Kruskal(graph);
printf("total_Cost: %d", total_cost);
}
'자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 중앙대 자료구조 👨💻Assignment 2_BST(이진탐색트리)구현(c언어) (0) | 2022.05.23 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조_스택을 활용한 미로찾기(대각선 이동 가능) (0) | 2022.05.09 |